2 min read
Curiosity Blog, Sols 4649-4654: Ridges, Hollows and Nodules, Oh My

Written by Lucy Thompson, Planetary Scientist and APXS Team Member, University of New Brunswick, Canada
Earth planning date: Friday, Sept. 5, 2025
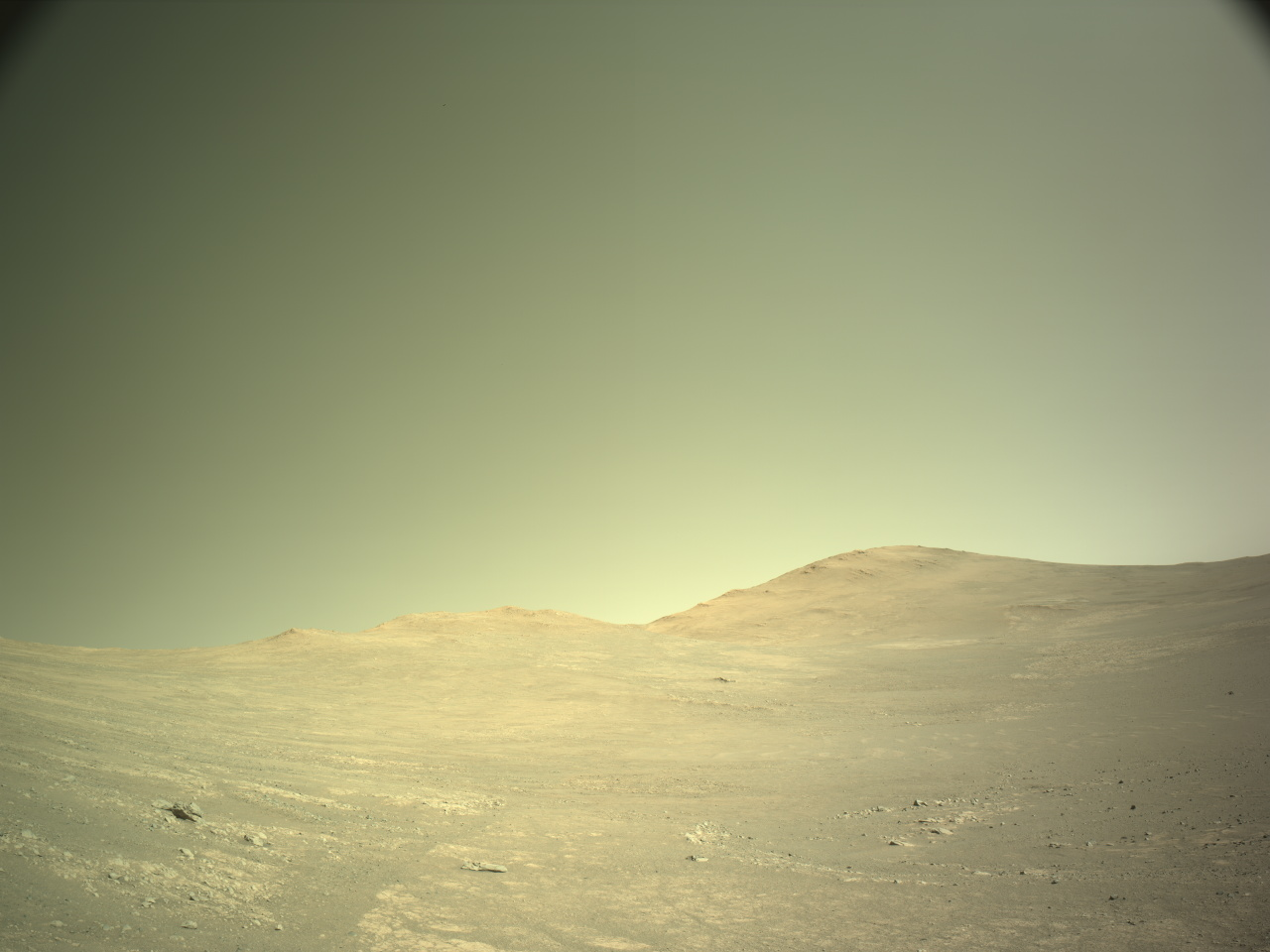
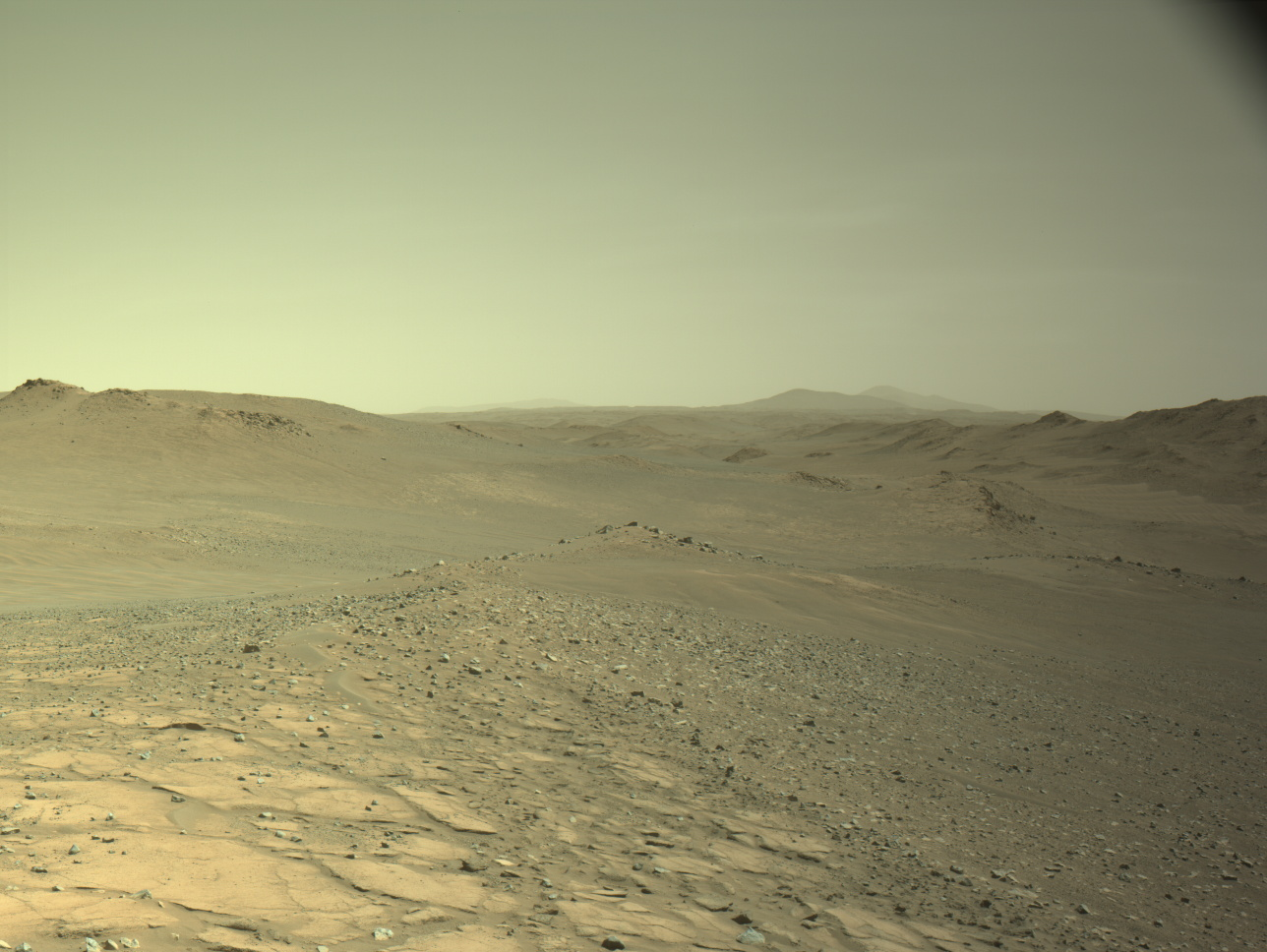
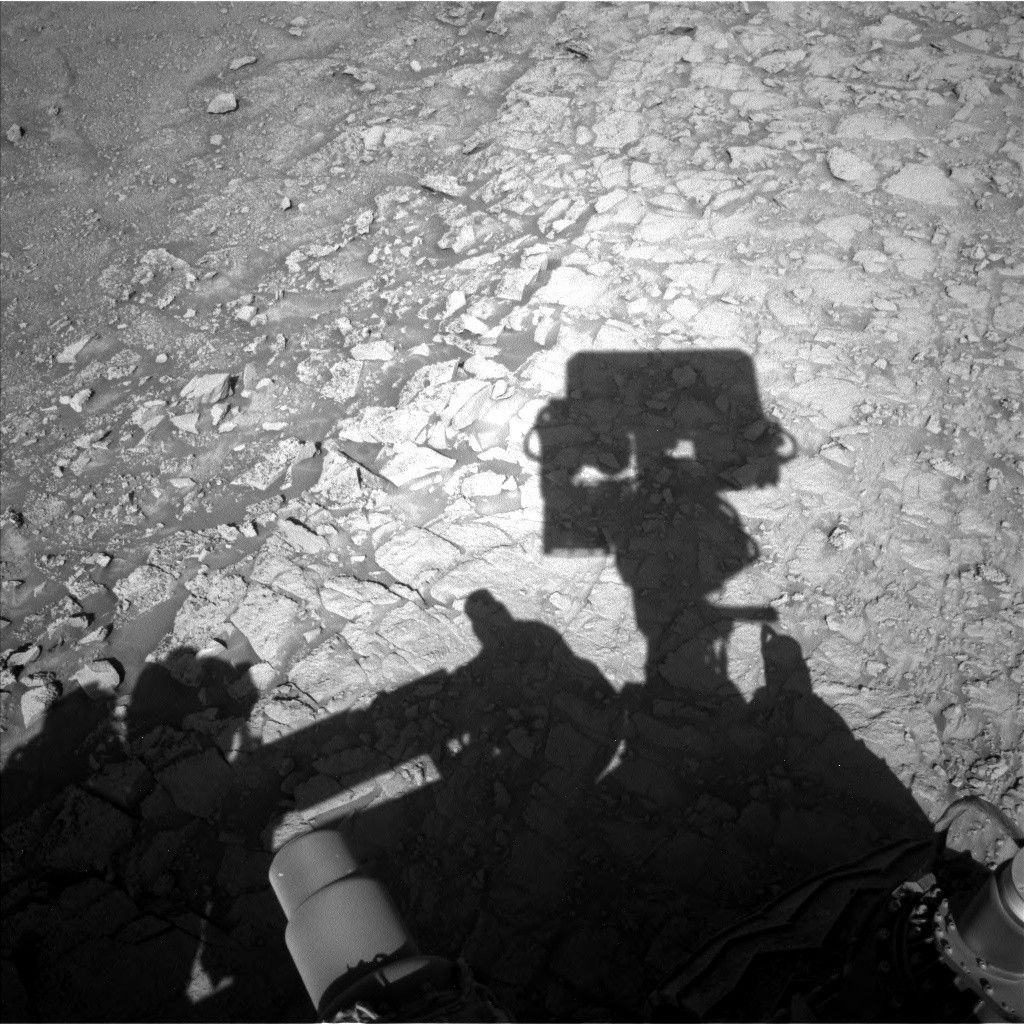
Curiosity is in the midst of the boxwork campaign, trying to decipher why we see such pronounced ridges and hollows in this area of Mount Sharp. When this terrain was first identified from orbit it was hypothesized that the ridges may be the result of cementation by circulating fluids, followed by differential erosion of the less resistant bedrock in between (the hollows that we now observe).
We have been exploring the boxwork terrain documenting textures, structures and composition to investigate potential differences between ridges and hollows. One of the textural features we have observed are nodules in varying abundance. The focus of our activities this week was to document the transition from smoother bedrock atop a boxwork ridge to more nodular bedrock associated with the edge of a shallow hollow.
In Tuesday’s three-sol plan we analyzed the smoother bedrock within the ridge, documenting textures with MAHLI, Mastcam, and ChemCam RMI, and chemistry with ChemCam LIBS and APXS. Curiosity then successfully bumped towards the edge of the ridge/hollow to place the more nodular bedrock in our workspace. Friday’s three-sol plan was basically a repeat of the previous observations, but this time focused on the more nodular bedrock. The planned drive should take us to another boxwork ridge, and closer to the area where we plan to drill into one of the ridges.
As the APXS strategic planner this week, I helped to select the rock targets for analysis by our instrument, ensuring they were safe to touch and that they met the science intent of the boxwork campaign. I also communicated to the rest of the team the most recent results from our APXS compositional analyses and how they fit into our investigation of the boxwork terrain. This will help to inform our fast-approaching decision about where to drill.
Both plans included Mastcam and ChemCam long-distance RMI imaging of more distant features, including other boxwork ridges and hollows, buttes, the yardang unit, and Gale crater rim. Planned environmental activities continue to monitor dust in the atmosphere, dust-devil activity, and clouds. Standard REMS, RAD, and DAN activities round out the week’s activities.

Explore More
Discover More Topics From NASA
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun, and the seventh largest. It’s the only planet we know of inhabited…

All Mars Resources
Explore this collection of Mars images, videos, resources, PDFs, and toolkits. Discover valuable content designed to inform, educate, and inspire,…

Rover Basics
Each robotic explorer sent to the Red Planet has its own unique capabilities driven by science. Many attributes of a…
Mars Exploration: Science Goals
The key to understanding the past, present or future potential for life on Mars can be found in NASA’s four…





